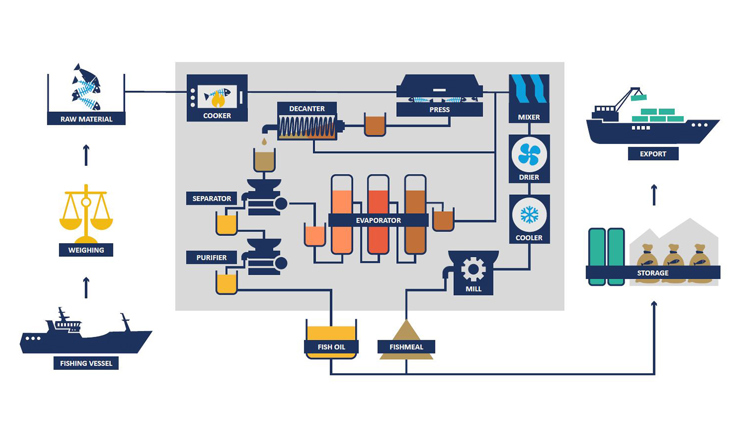
Raw material and intake
The raw materials delivered to FM and FO factories are composed of direct landings from fishing vessels, trimmings/by-product from fish processing industry and trimmings/by-product from the aquaculture industry. To optimize the quality of the final product, most of the fish supplied directly from fishing vessels is maintained in a chilled condition from the time it is caught until it is offloaded from the vessel.
Cooking
After the raw material is unloaded and stored in a buffer silo, the raw material is fed into a cooker. The raw material is heated to 90-95 ⁰C, which sterilizes the fish, coagulates the proteins and disrupts the cell membranes, to facilitate the separation of the soluble and the oil from the dry matter. The cooking temperature is controlled automatically to ensure correct cooking. This is done according to the veterinary approval.
Press & decanting
The cooked raw material is fed to either a screw press, a 2 phase or 3 phase decanter, where much of the liquid is squeezed out to produce a liquid phase, a solid phase, and if there is a 3 phase decanter, there is an oil phase.
Strainers are used before pressing to make optimal working conditions for the presses.. Efficient pressing gives low fat levels in the product. It is best practise within the industry that vapours from the pressing process are extracted for odour treatment.
Separator
The press water is separated further in a decanter. The press water contains most of the oil from the fish and dissolved proteins, salts and fine particles. The liquid from the decanter is sent to separators, where the oil is removed and subsequently stored for export.
A Two-step separation is used for fish oil extraction. 1) Extraction of oil from soluble fraction by means of separator; 2) polishing of extracted fish oil by means of second separator. All solids separated by this process are recovered.
Evaporator
The liquid that remains after the removal of the oil, is the stickwater. This is fed to evaporators, where it is concentrated before being blended with the presscake during the drying stage. The stickwater contains both dissolved and undissolved proteins, residual oil, minerals, and vitamins. To concentrate the stickwater and achieve a high concentration of dry matter, large quantities of water are removed by evaporation, which requires energy and the resultant condensate has to be discharged.
The industry currently uses various devices for evaporation and having an evaporator significantly reduces the environmental impacts of waste water to the receiving environment.
Dryer
The purpose of the drying process is to convert the wet mixture of presscake, decanter sludge and concentrated stickwater into a dry fish meal. In practice, this means drying to a moisture content below 12%, which generally may be considered low enough to inhibit microbial activity. This drying is done by heating the material to a temperature where the rate of evaporation of the water is considered satisfactory in order to avoid reduction of quality, especially of the protein.
Cooling
After drying the fishmeal is cooled. The fishmeal is cooled by air. Air for cooling is treated to reduce odour.
Grinder/Milling
The fishmeal is ground to a specific particle size using hammer mills. After the milling, the meal is stored for export either as meal or pelletized. Air from the grinding/milling are treated to reduce odour.